Poster Session
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Poster Session A
Session: (0115–0144) Antiphospholipid Syndrome Poster
0141: Cytokine profiles in antiphospholipid syndrome
Sunday, October 26, 2025
10:30 AM - 12:30 PM Central Time
Location: Hall F1
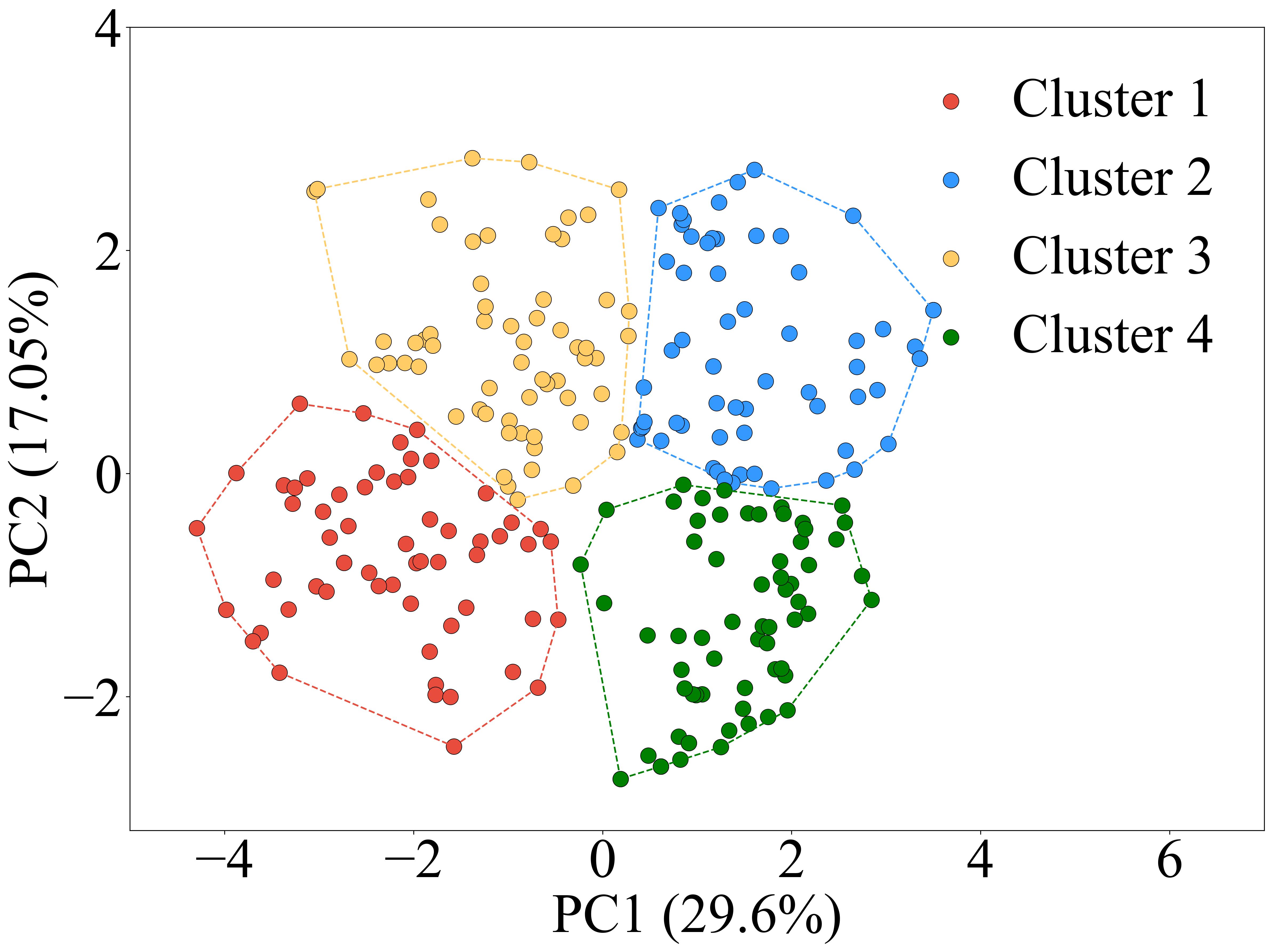
PCA scatter plot in patients with APS.
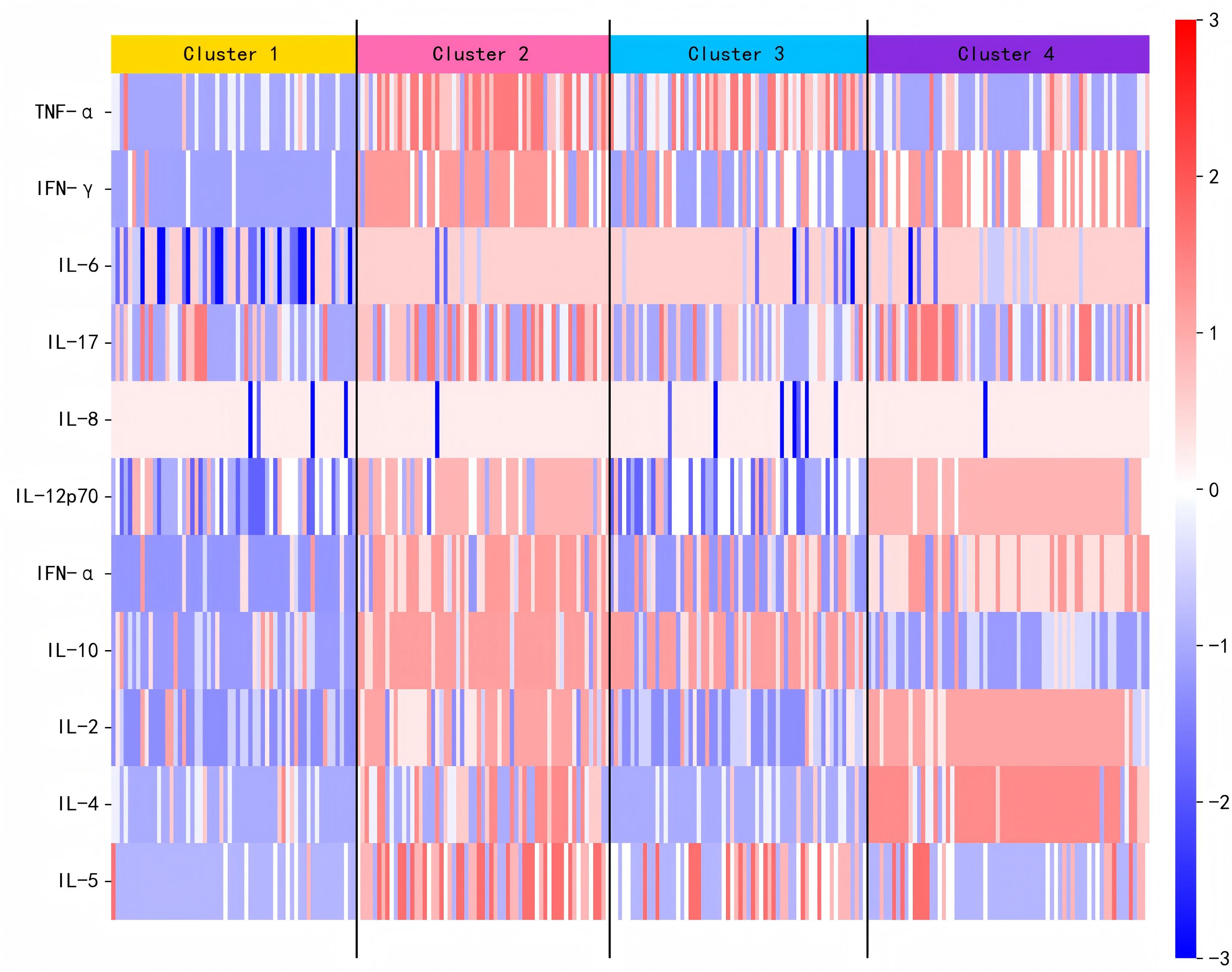
Heatmap of cytokine expression profiles across APS patient clusters.
- XL
Xiangjun Liu, MBBS
Peking University
Beijing, Beijing, ChinaDisclosure(s): No financial relationships with ineligible companies to disclose
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Background/Purpose: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease with unknown etiology. Inflammatory-mediated tissue damage plays an important role in APS. This study aimed to investigate the cytokine profiles in patients with APS.
Methods: Serum samples were collected from 250 patients with APS and 129 healthy controls (HCs). Serum concentrations of 11 cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-17, interferon (IFN)-α, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) -a, and IFN-γ,were measured by multiplex bead array assay. Principal component analysis (PCA) and K-means clustering were performed to stratify APS patients into distinct subgroups based on their cytokine profiles. Subsequent comparative analyses assessed differences in clinical manifestations and laboratory parameters across the identified clusters.
Results: Compared withHCs, APS patients displayed significantly increased levels of IL-2 (p = 0.040), IL-1β (p<0.001), IL-12p70 (p <0.001), IL-8 (p <0.001), IL-6 (p <0.001) and IFN-γ(p=0.012), and significantly decreased levels of IL-5 (p<0.001), IL-17 (p=0.007) and TNF-α (p=0.002). The patients with thrombotic APS had significantly higher levels of IL-6 (p < 0.0001), IL-10 (p = 0.005) and TNF-α (p = 0.01), compared to patients with obstetric APS. Unsupervised clustering identified four distinct subgroups (Fig. 1): Cluster 1 (N=59) with globally suppressed cytokines except moderate IL-8; Cluster 2 (N=61) exhibiting pan-hypercytokinemia; Cluster 3 (N=62) showing elevated TNF-α/IL-6/IL-10/IL-5 with suppressed IFN-γ/IL-17/IL-12p70/IFN-α/IL-2/IL-4; and Cluster 4 (N=68) characterized by IL-2/IL-4 overexpression (Fig. 2). Clinically, Cluster 2 correlated with higher aGAPSS scores, while Cluster 4 was enriched for primary APS (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: APS patients show distinct cytokine patterns with thrombotic cases displaying stronger inflammation. Cytokine clustering identifies high-risk subgroups, suggesting utility for patient stratification.

